Talk:Substituted 3-hydroxyisoxazoles
Substituted 3-hydroxyisoxazoles (also known as 3-hydroxyisoxazoles, 3-isoxazolols or 3-isoxazolones) is a chemical class of organic compounds based on the 3-hydroxyisoxazole structure. Members of this class typically act on GABA and glutamate receptors. The best known members of this class are muscimol and ibotenic acid, alkaloids from Amanita muscaria, gaboxadol, a synthetic derivative of muscimol, and AMPA, a synthetic AMPA receptor agonist[1].
Chemistry
3-Hydroxyisoxazoles are a class of organic compounds that feature an isoxazole ring substituted with a hydroxyl group at the 3-position. The isoxazole ring itself is a five-membered heterocycle containing an oxygen atom and a nitrogen atom in adjacent positions. 3-Hydroxyisoxazoles can exhibit tautomerism, where the hydroxyl group can tautomerize to a keto form, resulting in a 3-isoxazolone structure.
Pharmacology
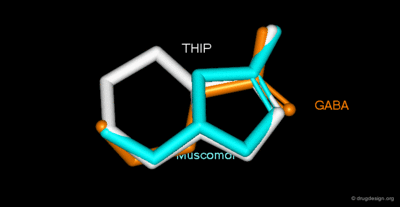
Most of the known 3-hydroxyisoxazoles may be regarded as conformationally restricted bio-isosteres of neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamic acid or N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA)[2]. Muscimol, gaboxadol and GABA are in their bioactive conformations, because of this similarity, muscimol and gaboxadol bind to certain GABA-receptors.
List of substituted 3-hydroxyisoxazoles
| Compound | R4 | R5 | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muscimol | H | CH2NH2 | |
| Ibotenic acid | H | CH(NH2)C(O)OH | |
| Gaboxadol | CH2CH2- | CH2NH- |