Histamine
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Histamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter that is involved with the immune system. It triggers responses due to inflammation or allergies.
It is responsible for dilating the blood vessels, lowering blood pressure, constricting the airways, production of gastric acid and for the sensation of itching.
Chemistry
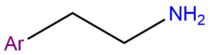
Histamine is a monoamine; it has an amine group attached to an imidazole ring via an ethyl chain. This monoamine chain can be found in many neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline. It's also found in many drugs, examples being tryptamines and phenethylamines.
See also
External links
References
This article does not cite enough references. You can help by adding some. |